
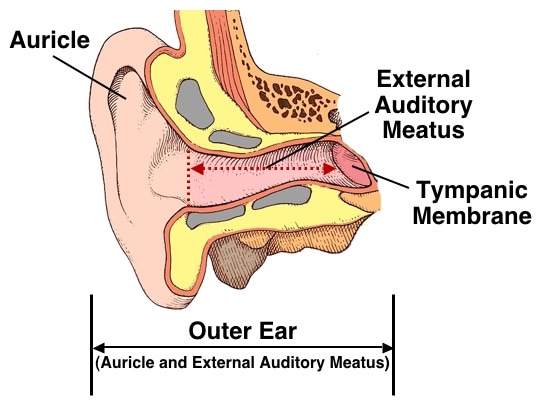
Injury to the round window (e.g., violent nose blowing, barotrauma while diving) causes sensorineural hearing loss. Vibrations of the footplate of the stapes are transmitted to the round window through the perilymph, which causes it to vibrate in the opposite phase of the oval window. A membrane-covered opening in the middle ear that lies below the stapes-covered oval window. An opening located in the middle ear at the base of the cochlea through which sound waves are transmitted to the inner ear. Connected to the nasopharyngeal cavity via the eustachian tube. Contains ossicles, muscles, and nerves (e.g., chorda tympani ). Air-filled space that is located within the petrous portion of the temporal bone. Function: transmits sound waves from the air to the ossicles and then to the inner ear. Consists of: tympanic cavity, mastoid process, and eustachian tube. Definition : : The middle portion of the ear that is located internal to the tympanic membrane and external to the oval window of the inner ear. Mechanical cleansing of the external auditory canal can lead to nausea and coughing! The area behind the auricle and the external auditory canal are innervated by the glossopharyngeal and vagus nerve. Function: Sound waves cause vibration of the tympanic membrane, which in turn transmits these vibrations to the ossicles of the middle ear (i.e., the malleus, incus, and stapes). Cone of light: a cone-shaped light reflection of the otoscope light in the anterior inferior quadrant, which helps with orientation. Umbo: the point where ossicles attach to the tympanic membrane. Cutaneous outer, fibrous middle, and mucous inner layer. Function: transmission of sound waves to the tympanic membrane. Epithelium contains ceruminous glands that produce cerumen ( ear wax): yellow-brownish, waxy, bactericidal secretion. Lined by thin keratinized stratified squamous epithelium along the entire canal also covers the external tympanic membrane. The outer third is formed by cartilage, the inner two thirds are formed by bone. External auditory meatus (auditory canal). Function: collects sound waves important for directional hearing. Definition: the external portion of the ear. It transmits information to the brain via the vestibular nerve. #Acoustic meatus registration#
The organ of Corti is responsible for sound detection, and it transmits auditory information to the brain via the cochlear nerve, while the vestibular system is responsible for the registration of body movement and spatial orientation. The inner ear is a fluid-filled cavity that contains the organ of Corti and the vestibular system. The ossicles amplify the resulting vibrations and transmit them to the inner ear via the oval window. The auricle captures sound waves and directs them through the external auditory canal towards the tympanic membrane, thus setting it in motion.
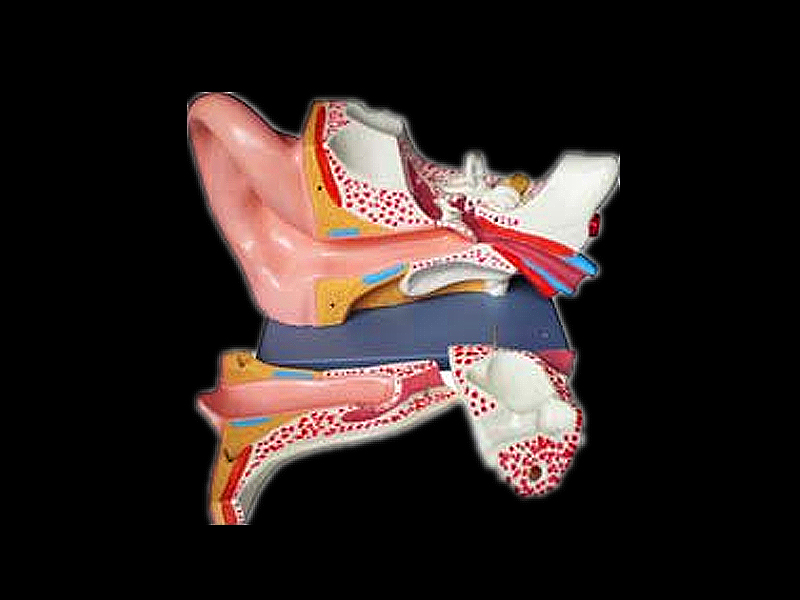
The eustachian tube connects the middle ear to the nasopharynx, equalizing the pressure between the middle ear and the atmosphere. The middle ear is a hollow structure that comprises the tympanic cavity, the ossicles, and the eustachian tube. The outer ear comprises the auricle ( pinna), external auditory meatus (auditory canal), and tympanic membrane ( eardrum), which separates the outer ear from the middle ear. It is divided into three sections: the outer, the middle, and the inner ear. The ear is the organ of hearing and balance.






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
